As an extreme example of the difference between risk ratio and odds ratio, if action A carries a risk of a negative outcome of 999% while action B has a risk of 990% the relative risk is approximately 1 while the odds ratio between A and B is 102/19/18 · While odds are expressed in the ratio, the probability is either written in percentage form or decimal Odds usually ranges from zero to infinity, wherein zero defines impossibility of occurrence of an event, and infinity denotes the possibility of occurrence Conversely, probability lies between zero to oneCheck https//wwwmathwithmennonl/Volg Math with Menno op Instagram https//wwwinstagramcom/mathwithmenno/?hl=nl Blij met mijn vi
Faq How Do I Interpret Odds Ratios In Logistic Regression
Log odds vs odds ratio
Log odds vs odds ratio-10/27/17 · then the odds ratio is computed by taking the ratio of odds, where the odds in each group is computed as follows OR = (a/b) / (c/d) As with a risk ratio, the convention is to place the odds in the unexposed group in the denominatorValue As a verb rate is to assign or be assigned a particular rank or level or rate can be to berate, scold



Statquest Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube
9/2/ · The risk or odds ratio is the risk or odds in the exposed group divided by the risk or odds in the control group A risk or odds ratio = 1 indicates no difference between the groups A risk or odds ratio > 1 indicates a heightened probability of the outcome in the treatment group The two metrics track each other, but are not equal8/7/14 · An example of what I am talking about is the choice between risk ratio and odds ratio Odds ratio vs risk ratio You know the difference between risk and odds A risk is the proportion of subjects with an event in a total group of susceptible subjects Thus, a RR of 25 would mean that the group in the numerator has a 150% greater chance ofOdds Ratio (OR) measures the association between an outcome and a treatment/exposure Or in other words, a comparison of an outcome given two different groups (exposure vs absence of exposure) OR is a comparison of two odds the odds of an outcome occurring given a treatment compared to the odds of the outcome occurring without the treatment
Englishwise, they are correct it is the odds and the odds are based on a ratio calculation It is not, however, the odds ratio that is talked about when results are reported The odds ratio when results are reported refers to the ratio of two odds or, if you prefer, the ratio of two odds ratios That is, let us write5/19/ · Figure2 Odds as a fraction Odds should NOT be confused with Probabilities Odds are the ratio of something happening to something not happeningIn our scenario above, the odds are 4 to 6 Whereas, Probability is the ratio of something happening to everything that could happenSo in the case of our chess example, probability is 4 to 10 (as there were 10 gamesOdds Ratios and Log(Odds Ratios) are like RSquared they describe a relationship between two things And just like RSquared, you need to determine if this
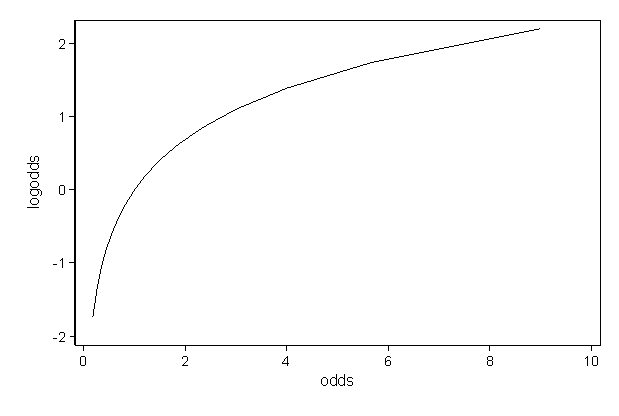
Inference from odds ratio If Then odds ratio = 1 the event is equally likely in both groups odds ratio > 1 the event is more likely in Group 1 odds ratio < 1 the event is more likely in Group 2 the greater the number the stronger the association In example 1 odds ratio = 36 students are much more likely to drink beer than teachers!8/21/14 · Odds ratio er innen statistisk forsøksmetode forholdet mellom to odds Odds ratio forkortes ofte OR En odds er sannsynligheten for at en gitt hendelse skal inntreffe i forhold til sannsynligheten for at den ikke skal inntreffe Hvis sannsynligheten for at hendelsen inntreffer er p, er sannsynligheten for at den ikke skal inntreffe (1−p) Da kan oddsen uttrykkes som brøkenDividing the former by the latter gives the log odds ratio Happily, we can take the antilogarithm of the odds, log odds ratio, a procedure called exponentiating, to get the odds ratio which is much easier to interpret This is just one odds divided by another odds
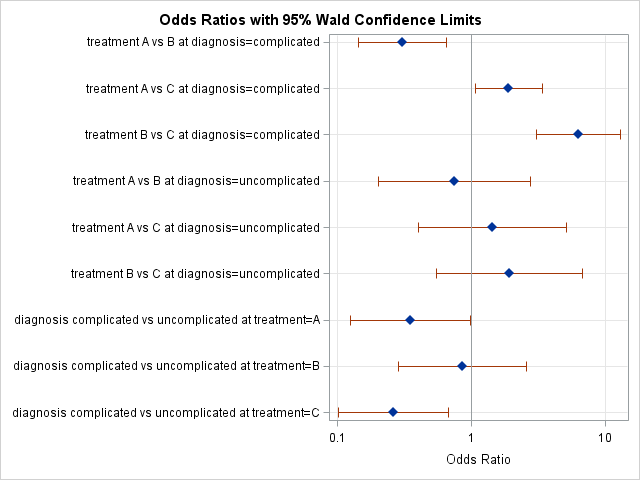


Odds Ratio Plots With A Logarithmic Scale In Sas The Do Loop



1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table
The odds ratio is a measure of effect size (as is the Pearson Correlation Coefficient) and therefore provides information on the strength of relationship between two variables It is an indirect measure however, as will be seen in the section on interpretation of the statistic8/26/ · Odds ratios While risk reports the number of events of interest in relation to the total number of trials, odds report the number of events of interest in relation to the number of events not of interest Stated differently, it reports the number of events to nonevents3/16/21 · In statistics, an odds ratio tells us the ratio of the odds of an event occurring in a treatment group to the odds of an event occurring in a control group Odds ratios appear most often in logistic regression, which is a method we use to fit a regression model that has one or more predictor variables and a binary response variable An adjusted odds ratio is an odds ratio that



Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube



Categorical Data Ziad Taib Biostatistics Astra Zeneca February
2/3/14 · The difference between odds ratio and risk ratio While Risk Ratio is the probability of one thing divided by the probability of another (usually in a separated group), Odds Ratio is the odds of one event happening divided by the odds of anotherOdds ratios and logistic regression When a logistic regression is calculated, the regression coefficient (b1) is the estimated increase in the log odds of the outcome per unit increase in the value of the exposure In other words, the exponential function of the regression coefficient (e b1) is the odds ratio associated with a oneunit increase in the exposure10/24/ · Odds can be expressed as a ratio of the probability an event will happen divided by the probability an event won't happen Odds in favor of A = A / (1 A), usually simplified to lowest terms, For instance, if the probability of an event occurring is 075, then the odds for it happening are 075/025 = 3/1 = 3 to 1 for, while the probability that it doesn't occur is 1 to 3 against



What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal



Diagnostic Odds Ratio Core Im Podcast
Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR)7/11/16 · The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio)When the disease is rare, the odds ratio will be a very good approximation of the relative risk The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk
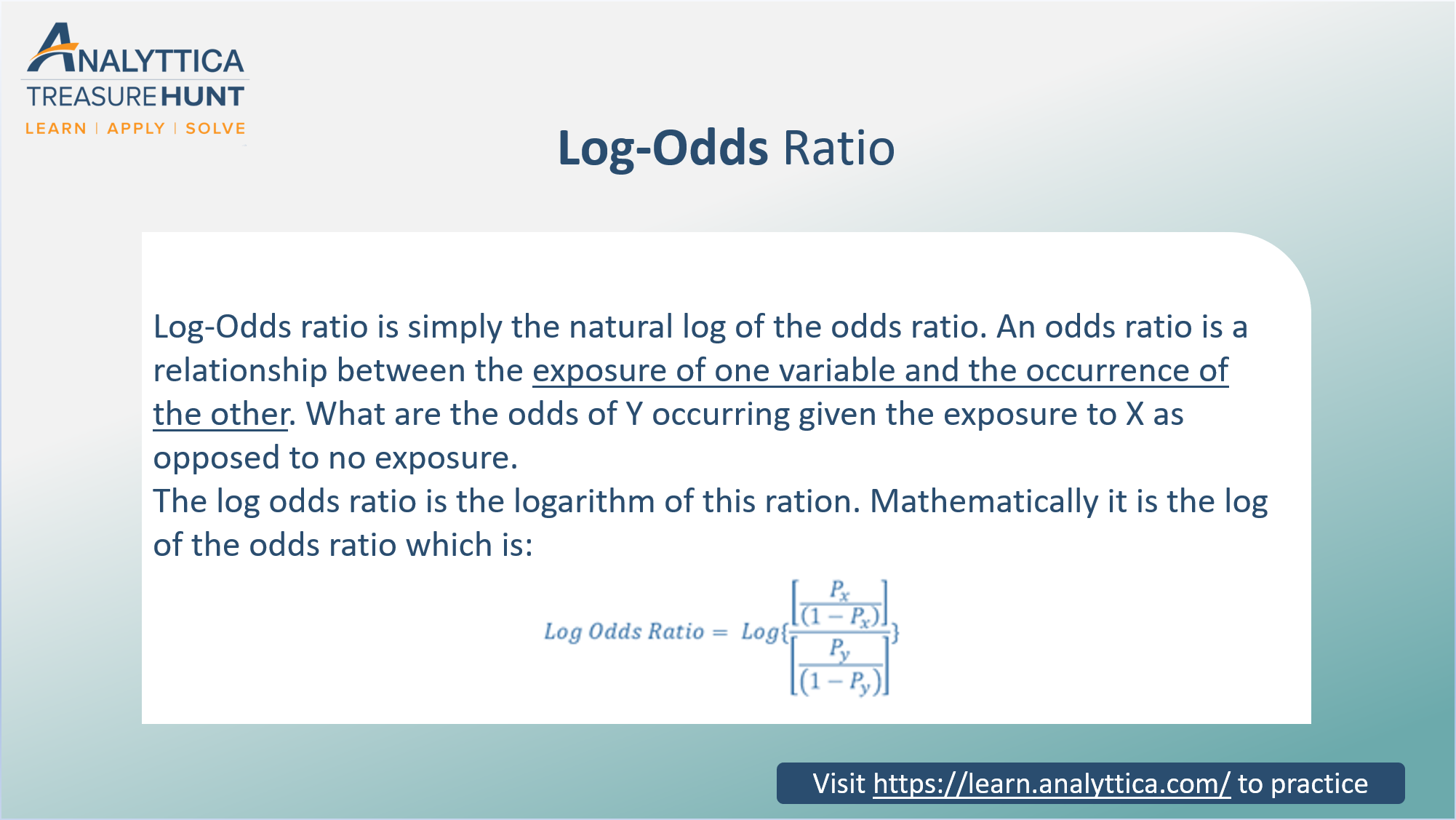


Log Odds Ratio Analytics Function Series By Analyttica Datalab Medium
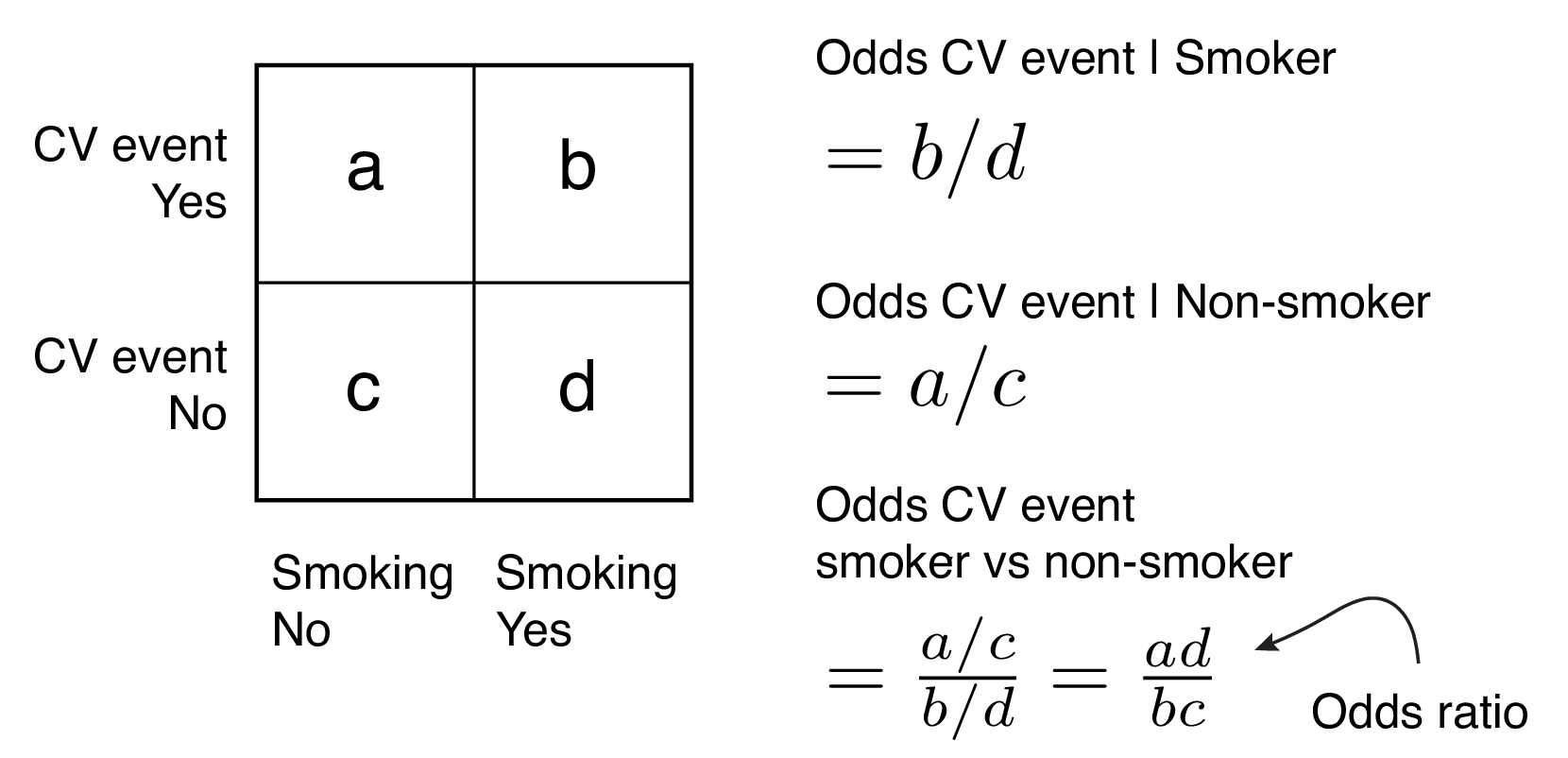


9 2 Binary Logistic Regression R For Health Data Science
1/4/19 · An odds ratio (OR) is a measure of association between an exposure and an outcome The OR represents the odds that an outcome will occur given a particular exposure, compared to the odds of the outcome occurring in the absence of that exposureMathematically, probability and odds ratio are two different things Probability is the likelihood that an event will occur, one side of a die out of six possible outcomes Odds ratio is the likelihood that an event will occur in relation to the likelihood that an event will not occur, 1 event for and 5 events against12/8/18 · Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio 80/100 people who use it get cancer /100 who don't use it get cancer The risk of getting cancer is 4 times greater in Vapalicious users RR = 08/02 = 4 Note how distorted the OR becomes in this example OR = (80/)/ (/80) = 16



What Is A Pooled Odds Ratio Quora
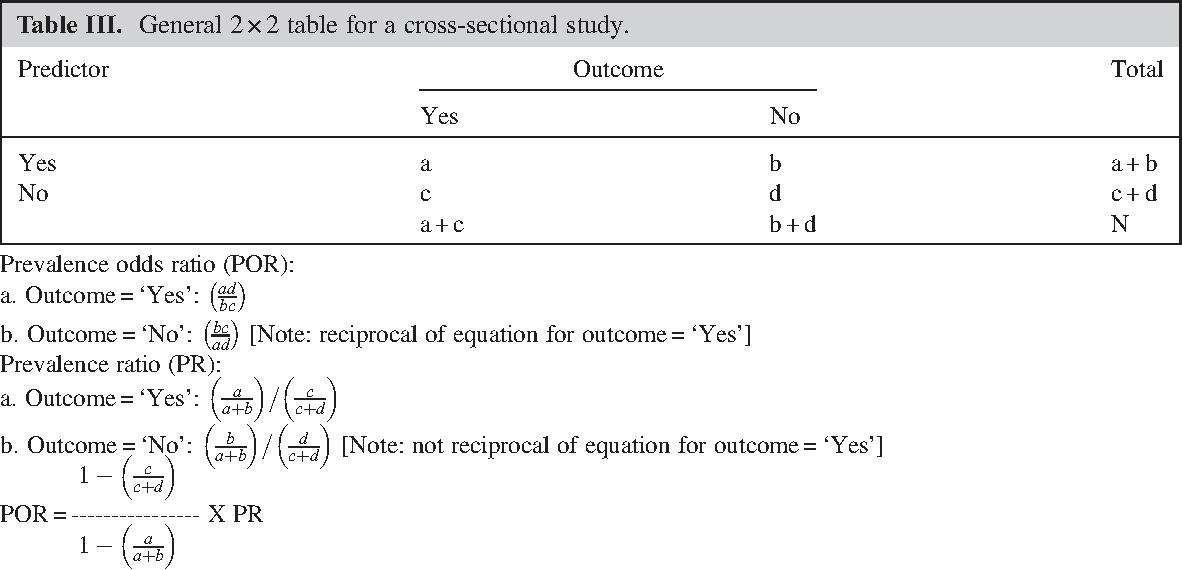


Pdf Prevalence Odds Ratio Versus Prevalence Ratio Choice Comes With Consequences Semantic Scholar
12/30/16 · Odds ratio (OR), risk ratio (RR), and prevalence ratio (PR) are some of the measures of association which are often reported in research studies quantifying the relationship between an independent variable and the outcome of interest There has been much debate on the issue of which measure is appropriate to report depending on the study designSlagen voor je examen?9/19/14 · Odds can have any value from zero to infinity and they represent a ratio of desired outcomes versus the field Odds are a ratio, and can be given in two different ways 'odds in favor' and 'odds against' 'Odds in favor' are odds describing the if an event will occur, while 'odds against' will describe if an event will not occur



Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj



Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk
Fractional odds are the ratio of the amount (profit) won to the stake;The ratio of the odds for female to the odds for male is (32/77)/(17/74) = (32*74)/(77*17) = 1809 So the odds for males are 17 to 74, the odds for females are 32 to 77, and the odds for female are about 81% higher than the odds for males7/1/17 · Odds ratio is a measure of association between two variables ie a measure to determine wether the presence of a variable is associated with the presence or absence of another variable For example, we can use odds ratio to measure if an exposure like texting while driving is associated with an outcome like RTA (Road Traffic Accidents)
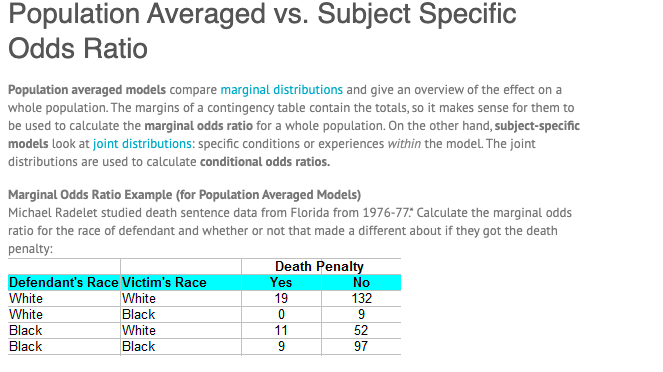


Population Averaged Vs Subject Specific Odds Rati Chegg Com
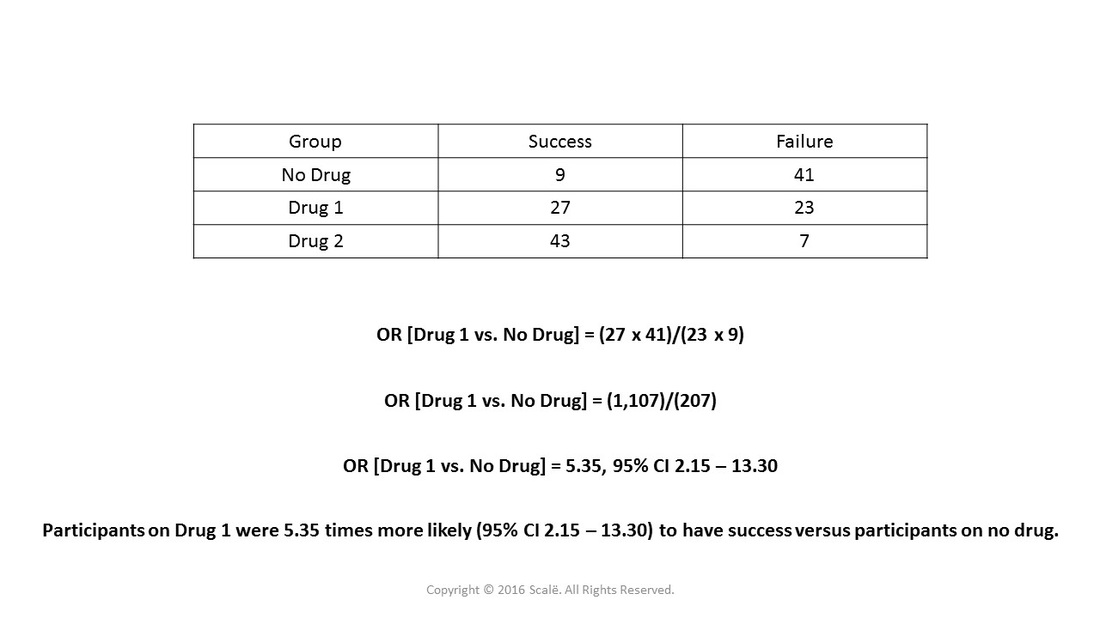


Use And Interpret Unadjusted Odds Ratio In Spss
As nouns the difference between odds and rate is that odds is the ratio of the probabilities of an event happening to that of it not happening while rate is (obsolete) the estimated worth of something;2/25/ · When looking at the association between binary variables, when are odds ratios better than risk ratios and viceversa?8/13/13 · An odds ratio is a relative measure of effect, which allows the comparison of the intervention group of a study relative to the comparison or placebo group So when researchers calculate an odds ratio they do it like this The numerator is the odds in the intervention arm The denominator is the odds in the control or placebo arm = Odds Ratio (OR)



Statquest Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube
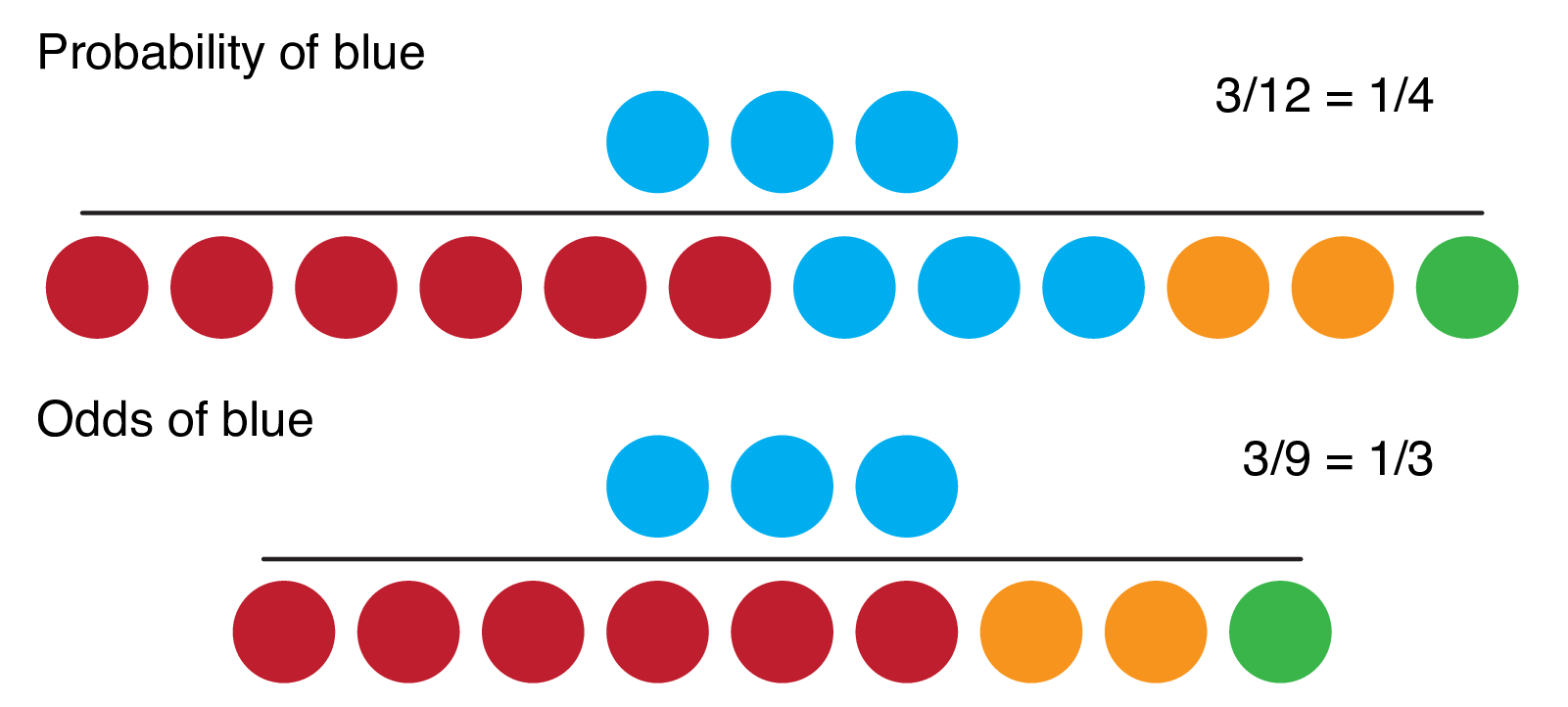


9 2 Binary Logistic Regression R For Health Data Science
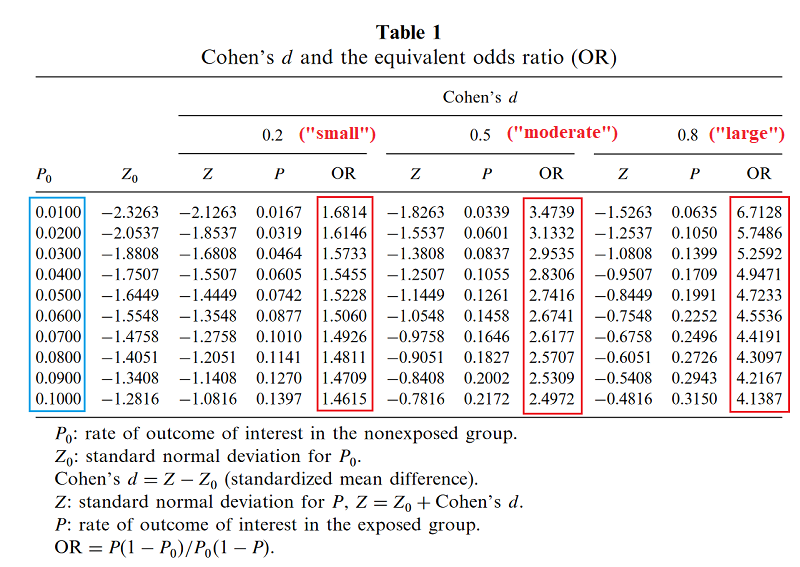
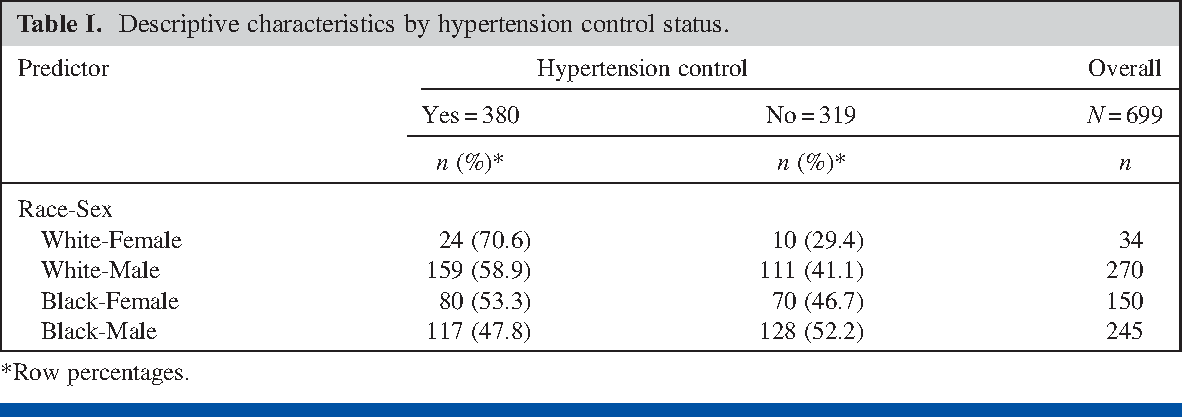
6 Converting Adjusted Odds Ratios to its RR counterpart7/27/ · This brings us to today's topic Odds Ratio (OR) vs Relative Risk (RR) Odds vs Probability why we love them and why these two cousin statistics continue to confuse us Anyone with a math, science, or medical background has been taught this, and if6// · In the previous article, we explained that the risk ratio (RR) and the odds ratio (OR) are measures of effect In this article, we will discuss in more detail the properties of the RR and the OR and how those 2 effect measures are related Table I summarizes risks, odds, RRs, and ORs



When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj



Odds Ratio Litfl Ccc Research
12/3/18 · When the Odds ratio is above 1 and below 2, the likelihood of having the event is represented as XX % higher odds (where XX % is Odds ratio 1) That means that if odds ratio is 124, the likelihood of having the outcome is 24% higher (124 – 1 = 024 ie 24%) than the comparison group6/1/12 · An odds ratio of 108 will give you an 8% increase in the odds at any value of X Likewise, the difference in the probability (or the odds) depends on the value of X So if you do decide to report the increase in probability at different values of X, you'll have to do it at low, medium, and high values of X3/2/ · The odds ratio is the ratio of two odds ODDS RATIO Odds Ratio = Odds of Event A / Odds of Event B For example, we could calculate the odds ratio between picking a red ball and a green ball The probability of picking a red ball is 4/5 = 08 The odds of picking a red ball are (08) / 1(08) = 08 / 02 = 4 The odds ratio for picking a red


Probability Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Gp Raj



Odds Ratios The Odd One Out Stats By Slough
Decimal odds represent the amount one wins for every $1 wagered The difference between the odds forOdds as a ratio (eg 43) Results Probability vs Odds Any chance can be numerically described as either odds or probabilities In the majority of circumstances, neither is preferable to the other The majority of scientists generally refer to probabilities, not odds, but that is more a matter of tradition, there is no logical basis for it10//18 · Summary Our theoretical Odds Ratio is 0319 with a CI(0, 041), which is close to the true Odds ratio, 03This indicates if the undergraduate students are from the school in prestige 3 or 4, the chances of them getting in graduate school is 38% that of the students from prestige 1 or 2 undergraduate schools



Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056



R Calculate And Interpret Odds Ratio In Logistic Regression Stack Overflow
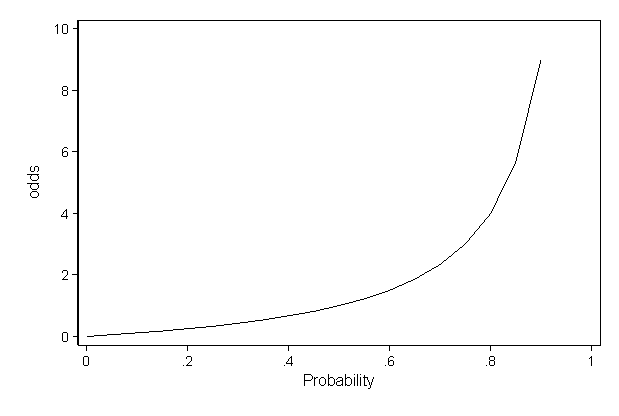
1/21/03 · Odds range from 0 to infinity, while probabilities range from 0 to 1, and hence are often represented as a percentage between 0% and 100% reversing the ratio switches odds for with odds against, and similarly probability of success with probability of failure



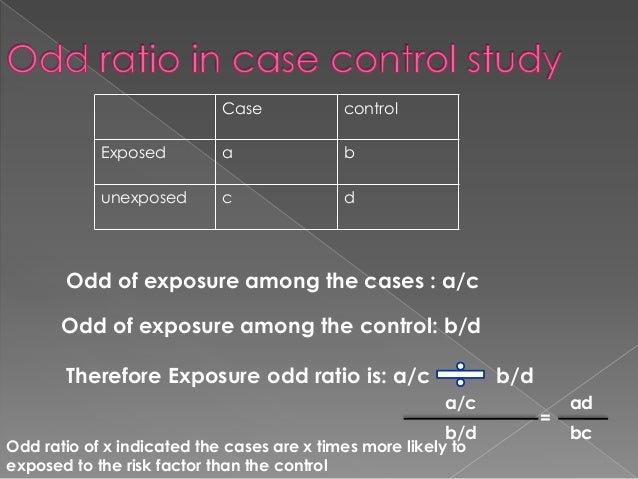
Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube



Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk


Odds Vs Probability Vs Chance Data Science Central



Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine



Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube



Ppt Chi Square And Odds Ratios Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Likelihood Ratio And Odds Ratio Slope Values Represent Odds As Shown Download Scientific Diagram


5 3 Marginal And Conditional Odds Ratios Stat 504



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Adjusted Odds Ratio Definition Examples


Logistic Regression Odds Ratio



Odds Ratio Article



Crude Odds Ratios Cor And Adjusted Odds Ratio Aor And Their 95 Download Table


Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 Ppt Video Online Download



How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube


Odds Ratio



On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk



Faq How Do I Interpret Odds Ratios In Logistic Regression


Use And Interpret Unadjusted Odds Ratio In Spss
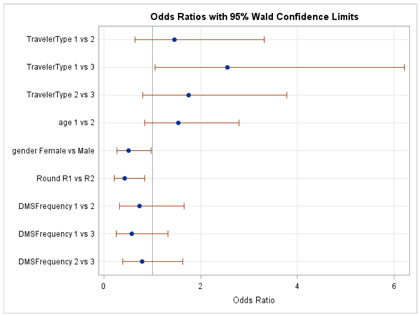


Public Perception Of Safety Messages And Public Service Announcements On Dynamic Message Signs In Rural Areas Appendix C Odds Ratio Graphs For Evaluation Of Hypotheses


Effect Modification Group C 1


Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios



Odds Ratio Wikipedia



A Most Odd Ratio American Journal Of Preventive Medicine



Odds Ratio Wikipedia



Odds Ratio Wikiwand



Plotting Odds Ratio Vs Continuous Variable In Stata Stack Overflow


Ctspedia Ctspedia Oddsterm



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1


Confluence Mobile Wiki Ucsf
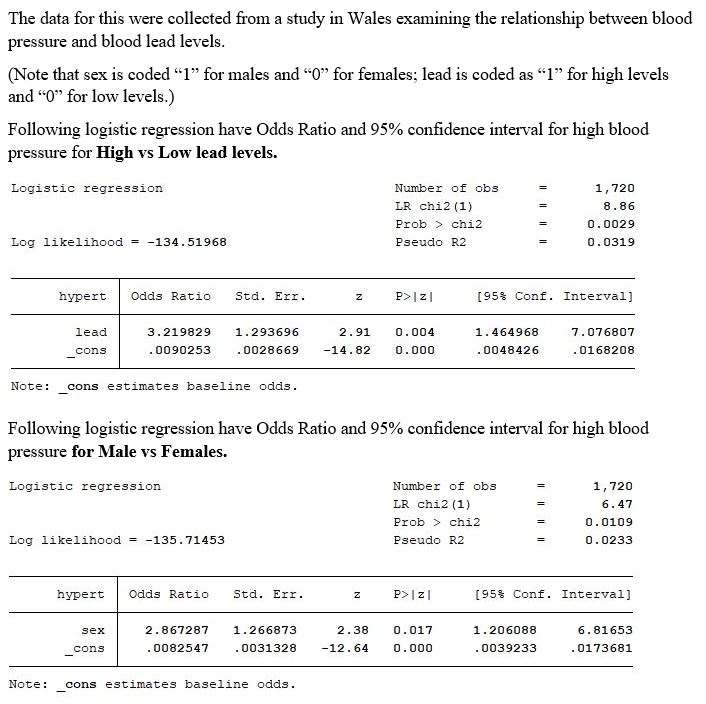


Solved 1 Based On The Information Provided Above Interp Chegg Com
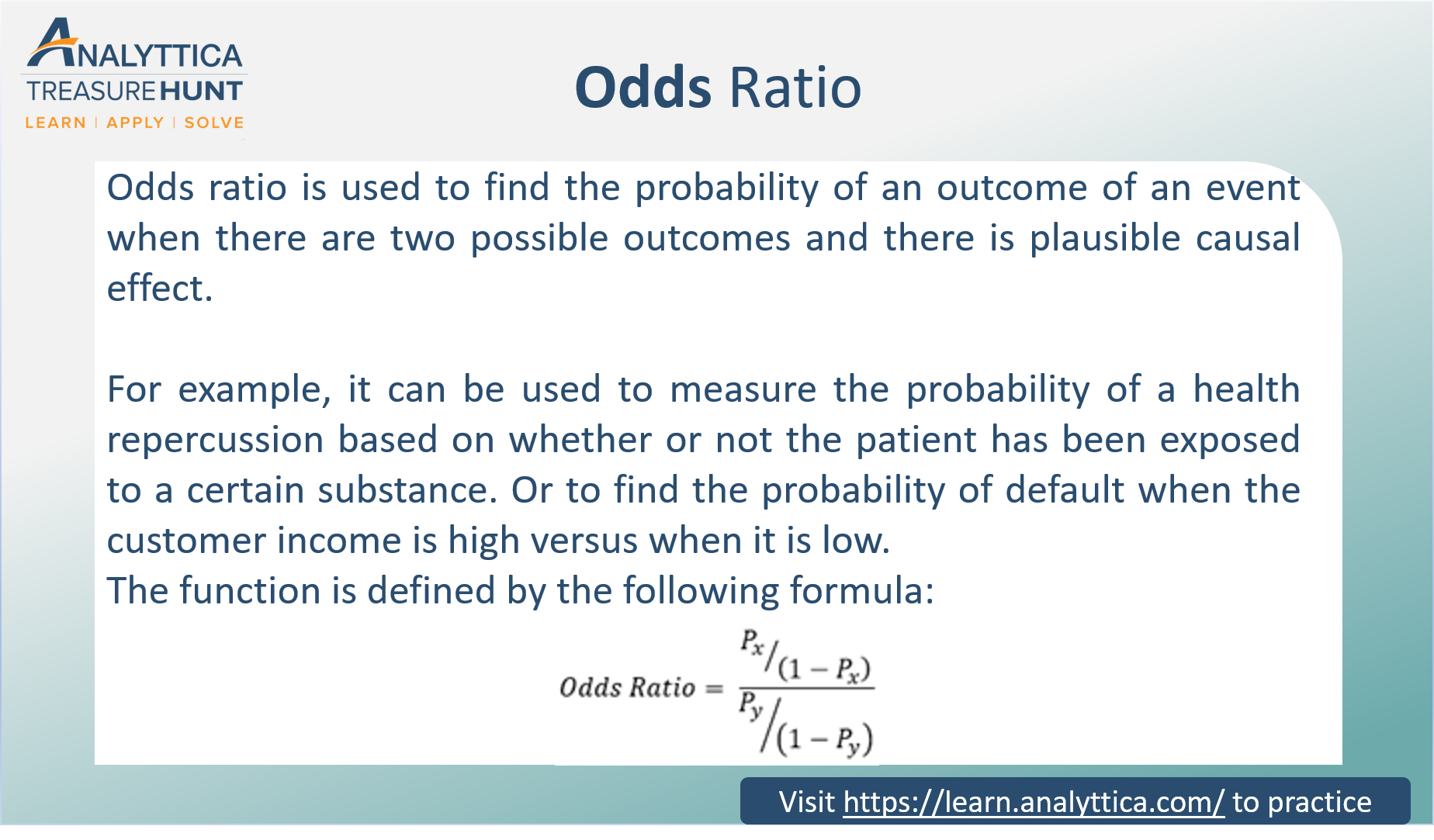


Odds Ratio The Odds Ratio Is Used To Find The By Analyttica Datalab Medium



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora
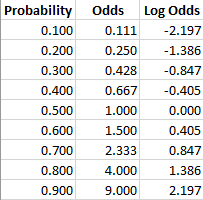


Log Odds Definition And Worked Statistics Problems



On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk



Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science


Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio Hunter 19 Notes And Things


Faq How Do I Interpret Odds Ratios In Logistic Regression



Fischer S Exact Test Odds Ratio And Confidence Intervals Jmp User Community


27 Sep 01 Draft



The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor



Strategies For Graphing Distributions Of Log Odds Estimates And The Corresponding Odds Ratios Cross Validated
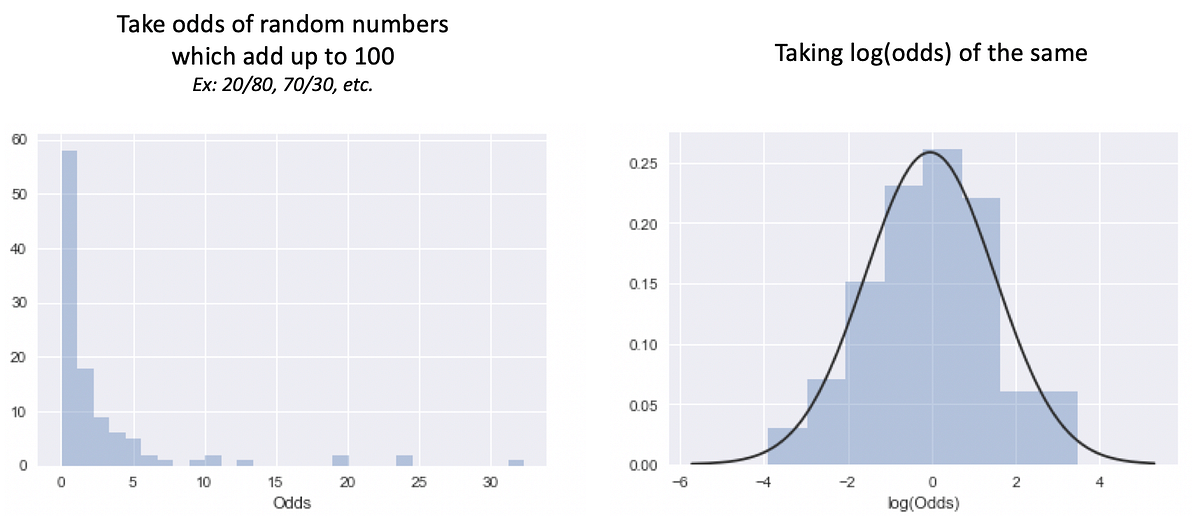


What And Why Of Log Odds What Are Log Odds And Why Are They By Piyush Agarwal Towards Data Science



A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence



Why Does Power Other Conditions Equal Decrease As The Odds Ratio Increases Above 2 Cross Validated



How To Get Odds Ratio In Ordinal Logistic Regression Jmp User Community



Diagnostic Odds Ratio Wikipedia
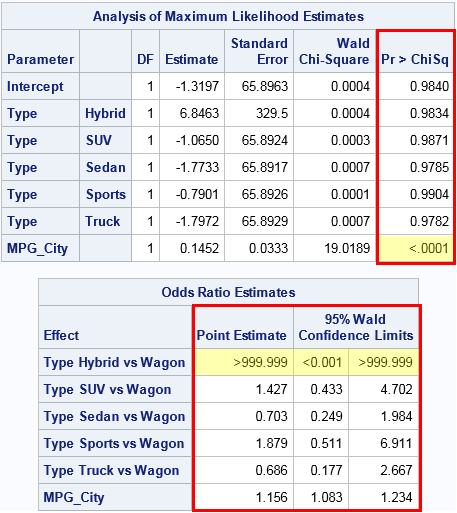


Formats For P Values And Odds Ratios In Sas The Do Loop


Odds Ratios Need To Be Graphed On Log Scales Andrew Wheeler
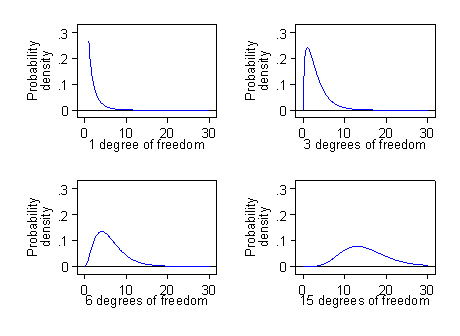


Proportions Chi Squared Tests And Odds Ratios



Math3010 Week 6



Graph Of Odds Ratio Versus Sleep Image Eurekalert Science News


Never Tell Me The Odds Ratio Slate Star Codex



What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal



A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence



Mixing Of Confounding And Non Collapsibility A Notable Deficiency Of The Odds Ratio American Journal Of Cardiology



Figure 7 Random Effects Model Meta Analysis Of Relative Odds Ratio Of Icd Vs No Icd For Arrhythmic Death Between Younger And Older Subgroups Assessment On Implantable Defibrillators And The Evidence For


Epidemiology Odds Ratio Or Bean Around The World



Cecile Janssens A Reminder That Odds Ratios Massively Overestimate Relative Risks When Outcome Is Common In The Population Or By Study Design E G Case Control Studies Io Is Proportion Of Cases



Odds Ratios Basic Concepts 12 638 Hygeia Analytics



Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy


Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo


Pdf Prevalence Odds Ratio Versus Prevalence Ratio Choice Comes With Consequences Semantic Scholar


Odds Ratio Osmosis



Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1


Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Authorstream



Logistic Regression With Interaction Odds Ratio Interpretation Cross Validated
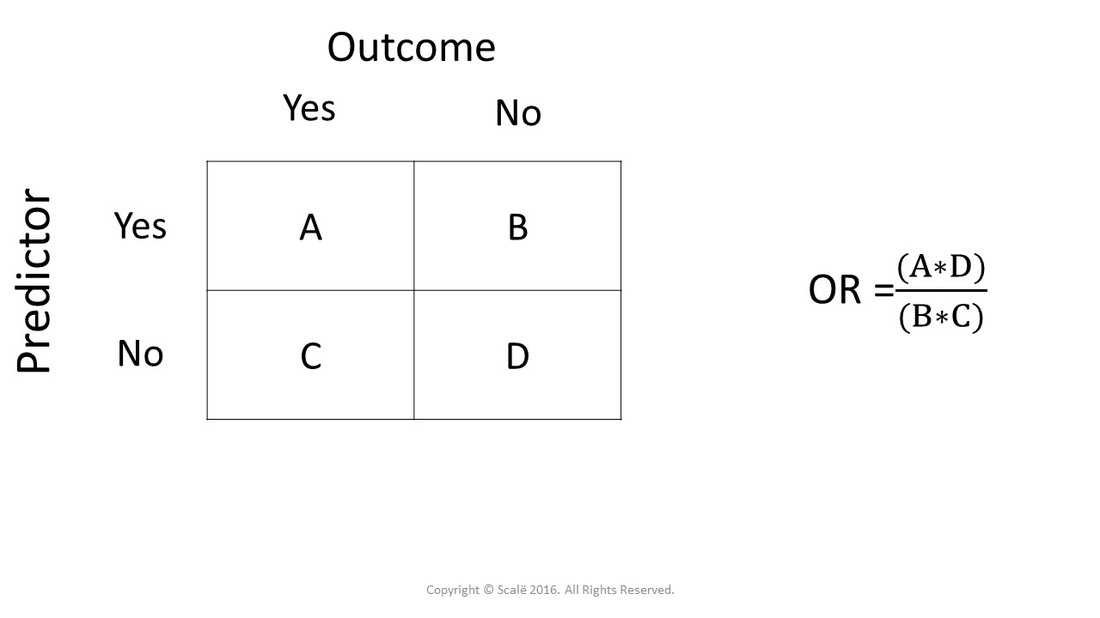


Calculate Odds Ratio With 95 Confidence Intervals



Odds Ratio Http Www Slideshare Net Terryshaneyfelt7 What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean Research Methods Academic Research Statistics Math



Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough



Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey



Cohort Specific And Meta Analysis Pooled Odds Ratios Ors Of Download Scientific Diagram



Odds Ratio Calculation And Interpretation Statistics How To



Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿